Assoc. Prof. Tran Chi Trung
Me.Nguyen Xuan Thinh, ME. Nguyen Van Kien
PIM Center
Summary: In general, irrigation management companies have had innovations in organization, management mechanism for exploitation irrigation systems creating favorable conditions for more effective performance of irrigation systems, closer to reality water demand of water users, however, governance quality of the irrigation management companies is generally low. Governance for management organization lacks science, so production costs are still high, fuel consumption is high, and labor productivity is low. This study proposes solutions to improve organizational structure and several governance mechanisms to improve governance quality of the irrigation management companies.
Keywords: Organizational structure, governance mechanisms, enterprise governance
- Introduction
According to results of reviewing and updating data up to date, whole country has a total of 96 irrigation management organizations, including 84 irrigation management companies (accounting for 85%), 3 irrigation management boards (3%), 8 irrigation management centers (8%) and 4 irrigation department (4%) are responsible for managing irrigation works. The irrigation management companies (IMC) include 3 IMCs under the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development managing inter-provincial irrigation system and 81 IMCs managing irrigation systems within province. The irrigation management companies are established in 48 provinces and cities nationwide, of which the Red River Delta provinces have 31 companies (accounting for 39%) of total number of companies while irrigated area of agricultural land is equal to 15.8% of country, while Mekong Delta currently has only 5 companies but provide water for 47.3% of irrigated agricultural land. Management and exploitation of irrigation works is gradually getting into order, serving agriculture production and people’s livelihood well. Therefore, managing and exploiting irrigation works basically meet requirements of serving production and people’s livelihood. However, governance quality of the irrigation management companies is generally low, production costs are still high, fuel consumption is high, labor productivity is low, business management is still administratively dictated, mainly implementing by planning mechanism.
Based on overview of related researches and results of investigation at 17 IMCs representing different regions in country (PIM Center, 2021), this article analyzes reality governance status of IMCs, thereby proposing solutions to improve governance quality of IMCs
- Current status of governance quality of IMCs
Enterprise governance is a process of continuous, organizational and purposeful influence from business owner to the employees. According to this concept, enterprise governance is considered process of effectively using potential, as well as opportunities to carry out production and business activities in an enterprise effectively. Enterprise governance is also a system of all rules, mechanisms and regulations that help operate and manage the enterprise. According to this concept, enterprise governance aims to balance interests of many stakeholders such as state agencies, business partners, employees, water users, environment and community. Accordingly, current state of enterprise governance of IMCs is assessed through two aspects: Management organization and documents, regulations for enterprise governance as below.
a) Management organization of IMCs:
Irrigation management companies established under Enterprise Law (2020) are one-member limited liability companies, owner is state holding 100% of company’s charter capital and has full rights to change organizational structure such as appointing, dismissed, hired business management all levels. The executive board of companies includes president or chairman of board of members, director and deputy directors and controllers. Most companies have 4-5 common management divisions including organizational-administrative, technical and works management, finance-accounting, planning and irrigation management divisions. These management divisions are in accordance with Decree 67/2018/ND-CP. Some companies have an internal control board, enterprise representative office or project investment board. Companies establish production units providing irrigation services as branches and irrigation stations. Some companies have production and business enterprises that perform other services, such as design consulting, construction, installation and works repair.
Survey results on labor at 17 IMCs show that average number of employees in companies is 401 persons, of which Hai Duong company has the largest number of employees at 1,490 persons, while some companies with a low number of employees such as My Thanh company with 88 persons and Binh Phuoc company with 98 persons. Total number of employees in most companies is equal or lower than approved technical-economic norms. There are many companies with relatively low average area per direct labor such as Binh Phuoc company 47ha/person, Nam Duong company 51ha/person. Average rate of indirect labor in companies is 19%, companies with high rate of indirect labor such as Ha Nam company up to 31%, Thua Thien-Hue company 27%, Nam Ninh company 25%.
b) Documents and regulations for enterprise governance
Although IMCs mainly operate for public irrigation services, but operating mechanism is implemented according to Enterprise Law and regulations for 100% state-owned enterprises in form of one-member limited liability companies. Common documents and regulations for operating and business management of IMCs are: Charter of operations, internal spending regulations and regulations on coordination of activities between company and localities. Some companies, such as Bac Song Ma company has regulations to encourage promotion of initiatives to reduce costs, improve operational efficiency and enhance company’s production and business efficiency. These regulations promote employees developing their abilities and initiatives to bring real efficiency to the company.
c) Assessment of actual enterprise governance of IMCs:
In general, IMCs have had innovations in organization, management mechanism for exploitation of irrigation systems creating favorable conditions for more effective performance of irrigation systems. Therefore, irrigation services have been improved, most of irrigation systems have been maintained to ensure safety, creating a stable source of irrigation water, increasing irrigation area, however governance quality of IMCs is generally low.
Main shortcomings leading to low governance quality of IMCs are:
- Many companies has average area per direct labor is quite low. Companies have low average area per direct labor, partly due to characteristics of irrigation works being decentralized and partly due to unreasonable and ineffective arrangement of labor. Companies are not interested in restructuring to improve operational efficiency through identifying job positions to reduce unnecessary workforce. Some companies have high rate of indirect labor, indicating need to review management structure and labor arrangements.
- Quality of human resources, including managers in many companies does not meet requirements, even in wrong job, so managing and exploiting irrigation works face many difficulties, not properly and fully complying with standards and regulations on irrigation management
- No autonomy on labor, human resources and salaries. Most companies have not yet developed job placement schemes and salary payment mechanisms for workers, recruitment, salary increase, promotion, arrangement and use of labor in company still depends on decision of the state.
- Production governance organization lacks science, so production costs are still high, fuel consumption is high and labor productivity is low.
- Lack of mechanism to encourage workers to operate economically and uncontrolled operation causing waste of water and electricity costs.
- Mechanism to bind rights and responsibilities of leader with effectiveness of using capital, assets, materials, labor is unclear causing waste of resources.
- Income distribution for workers is still uneven, leading to low labor productivity and high production costs.
- Approach to irrigation management is still inadequate as single-sector, mainly relying on funding support for public irrigation service from the state, companies have not proactively exploited the irrigation systems in an integrated manner.
- Scientific basis to improve quality of enterprise governance
a) Characteristics of management and exploitation of irrigation works:
- Irrigation management enterprises are state-owned enterprises that provide irrigation services as public services with complex operations, not as simple as enterprises providing products and services like other public services such as culture, healthcare, environmental sanitation, national security and defense. In same irrigation system, but when enterprises exploit irrigation works to provide water for production and business purposes other than for agriculture and people’s socio-economic livelihoods, that activity is purely commercial service, therefore. costs and prices is decided based on economic efficiency goals, scale. When enterprises provide irrigation services for agricultural production, people’s livelihood, and socio-economics, in addition to simply economic efficiency, social efficiency must also be considered. In years when there is drought, flooding, activities of enterprises are almost entirely for social purposes, production plans of enterprises are often affected by political factors. This is difference in production management organization of IMCs as compared to other conventional enterprises.
- Assets of the irrigation management organizations are mainly fixed capital invested in construction of works by the State. Irrigation works have great value but are spread over a large area causing difficult to manage and protect them. Moreover, irrigation systems are greatly affected by weather conditions and natural disasters, so quality and longevity of works will degrade very quickly if there is no mechanism to attach responsibility to operation workers with quality and longevity of irrigation works.
b) Principles for building management organization:
Organizational structure of IMCs needs to be organized compactly and flexibly, promoting effective management and exploitation of irrigation works. Main principles for building and organizing management of irrigation works include: Ensuring uniformity, integrated exploitation, multi-objectives with participation of relevant parties, optimality of management organizational structure, flexibility of structure and operational reliability and economics
c) Enterprise governance functions:
Enterprise governance has four main functions: strategic planning, organization, leadership management and control and adjustment. The key elements of these functions are:
- Strategic planning function: Business management needs to determine goals and plan strategies to achieve business goals. Planning function plays a role in determining development directions as well as predicting possibilities and planning implementation.
- Organizational function: Organizational function is mainly expressed through areas of organizational structure, personnel assignment, work assignment and resource allocation to divisions in the company; build and promulgate coordination mechanism within enterprise to ensure all activities are carried out in the most effective way.
- Management and leadership functions: Enterprise governance performs function of managing and leading human resources according to regulations. During this process, administrators carry out many activities related to mechanisms, policies, working styles and administration to encourage employees to work hard.
- Control and adjustment function: Business administrators regularly check and closely monitor business’s operating process, in order to objectively evaluate and promptly update company’s internal situation. During this process, enterprise governance helps to understand strengths and remaining shortcomings, thereby providing better solutions for adjustment and improvement.
- Solutions to improve quality of enterprise governance of IMCs
4.1 Solutions to perfect organization of IMCs
- Completing organizational structure of IMCs:
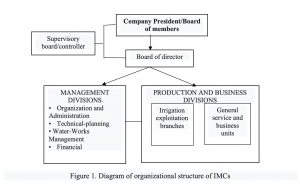
One-member limited liability ÍMCs can be established according to model of company director/general director or model of board of members, director/general director. Company’s management structure as seen in Figure 1 includes:
– Executive apparatus: Company chairman or chairman of board of members, director, deputy directors, controllers or control board.
– Management units: Companies should have 4-5 management units in accordance with Decree 67/2018/ND-CP. Main management units are the organizational-administrative, planning-technical, water-works management and finance departments.
– Units directly operating irrigation works: There is a need to review units under company, reorganize in direction of branches or stations to manage and operate according to hydraulic irrigation system to reduce number of units
– General business service units: In companies with large revenue potential from other irrigation service products, a business service department should be established and reorganized in accordance with scale of production. business output. This department is responsible for managing general business services advises and assists the board of directors in organizing, planning, promoting, calling for investors to exploit other irrigation services and supervising supply activities in providing other irrigation services. These activities operate according to market mechanisms, so marketing activities must be promoted, In addition, companies need to have other production and business enterprises to perform services such as design consulting, construction and installation and repair of works or seafood to increase revenue.
- Work specialization:
Specialization is a form of division of labor in which an assigned individual or group focuses their efforts on a certain area. In business management system, applying specialization helps increase productivity and work efficiency. Task of job specialization step is to identify functions and jobs necessary to realize strategic goals. Content and implementation process starts from analyzing strategic goals of IMCs, thereby forming functions that company needs and determining tasks that need to be implemented. Main company’s functions are determined based on regulations on management of irrigation works of the Irrigation Law (2020) and functions, tasks and jobs for IMCs are shown in Table 1.
In order to have compact and effective apparatus, thereby increasing income of workers of IMcs, number of workers needs to be in accordance with approved economic-technical norms. However, in long run, it is important that companies have authority and flexibility to adjust human resources and encourage employees to work effectively. At same time, it is necessary to ensure coordination, which means building a mechanism to coordinate activities of departments and mechanism to monitor results of coordination.
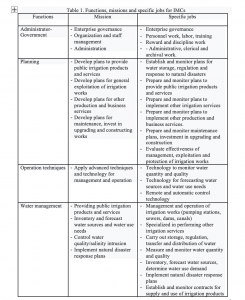
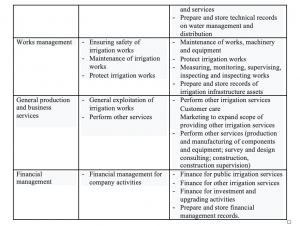
- Develop job placement scheme:
Companies building job placement scheme will have autonomy over labor and human resources, proactively recruit workers, raise salaries, upgrade ranks, arrange and use workers properly thereby reduce number of workers. Results of analysis and determination of jobs for IMCs in Table 1 are basis for determining job positions. Companies need to properly arrange workforce in terms of qualifications and number of specialized departments requiring high technology, branches and irrigation stations, thereby increasing productivity of each employee and improving company’s overall labor productivity. Labor arrangements should be suitable to each person’s strengths according to job position.
Labor for irrigation management is seasonal according to agricultural production season. During irrigation and drainage seasons, workers have to work all three shifts, but when there is time left, there is plenty of surplus labor. Management organization, arrangement and coordination of labor are difficult problems, therefore, it is necessary to have an appropriate labor management mechanism to improve operational efficiency of irrigation management and increase worker income
- Job position description:
There is a need to develop job position descriptions or job titles for all job positions in organizational structure. It should clearly state duties, powers, responsibilities, working conditions and specific requirements for personnel holding those positions. Job position description is also basis for evaluating performance of tasks publicly, transparently, fairly and objectively based on final results of each job.
4.2 Solutions to improve enterprise governance mechanisms
- Mechanism for assigning autonomy and self-responsibility in production and business to IMCs:
– It is necessary to give autonomy and self-responsibility to IMCs in terms of finance, labor use, production planning, joint ventures and income distribution.
– IMCs are given autonomy to decide on salaries and wages for managers, employees based on volume, results, work efficiency and responsibilities of each person according to internal spending regulations of the company.
– To create conditions for IMCs to exercise their autonomy and self-responsibility, it is necessary to support and give incentives to companies to carry out general business activities to maximize potential and advantages of irrigation systems for creating additional revenue for enterprise, gradually reducing subsidies from state budget
- Mechanism for assigning responsibilities to organization heads:
– The head of company has autonomy and self-responsibility in production activities and provision of other irrigation services such as proactively building strategies and business plans for other irrigation services to meet the needs of customers. market and in accordance with supply capacity of the company.
– Financial autonomy to ensure effectiveness of providing other irrigation services and autonomy and self-responsibility in joint ventures, production links, service provision and business without affecting activities providing public irrigation services
– Autonomy and self-responsibility for organizing and performing tasks such as recruiting and arranging labor properly; Mobilize capital and contribute capital to maximize potential of general business services.
– Decide to establish and reorganize general business services department in accordance with production and business scale of the company
– It is necessary to assign responsibility to the head of company in developing plan to exploit potential of irrigation works each year and consider this as an indicator to evaluate level of task completion associated with market mechanism, transparent reward
- Implement thorough contracting mechanism for groups and workers:
Contracting mechanism is highly feasible when applied in enterprises managing irrigation works. On the basis of approved economic-technical norms, it is necessary to specifically calculate volume of work and materials for operation and maintenance management, thereby implementing a thorough contracting mechanism to groups and workers to improve labor productivity, save fuel, materials and energy.
- Mechanism to create motivation to improve labor productivity:
Motivation is main reason to perform behavior as well as basis motivating people to do or not do a certain task. Motivation is an internal factor that stimulates people to work hard, creating high productivity and efficiency thereby promoting creativity and potential strength within human relationships and overcoming challenges. Some motivational mechanisms to improve labor productivity are proposed as below
i) Develop transparent and fair salary and reward regulations for employees based on work results (material motivation)
– Develop salary and reward regulations for employees to eliminate current “leveling” distribution mechanism according to the salary scale.
– Develop regulations for paying salaries and wages to employees in association with results of performing tasks monthly, quarterly, and annually according to principle of “work more, enjoy more, work less, enjoy less, no work, no reward” which is associated with increased income thanks to revenue from providing other products and water services.
– Increasing appropriate reward level associated with benefits gained for business creates motivation to stimulate workers to increase productivity and improved techniques to increase revenue for the business.
– At same time, there are clear regulations on penalty mechanisms if tasks are not completed
ii) Create friendly working environment (mental motivation)
– Build a friendly working environment, narrow gap between leaders and employees and create conditions for employees to have opportunity to present ideas, opinions and promote their own strengths and abilities
– Grasp wishes and concerns of employees, then take timely measures to resolve them to create a state of trust and peace of mind for the employees.
– Invest in equipment and additional facilities so that workers feel comfortable and feel secure in their work.
- Incentive mechanism for implementing initiatives:
It is necessary to develop regulations to encourage implementation of initiatives to reduce costs, improve operational efficiency and enhance company’s production and business efficiency, thereby motivating employees to promote their abilities and initiatives to bring benefits to the company. such as initiatives to increase revenue and effectively implement annual irrigation area, saving electricity for production. Therefore, a mechanism to promote innovations and ideas and honor contributions to businesses is necessary, people with initiatives need to be rewarded commensurate with cost reduction efficiency and production and business efficiency from their initiative effort applied
- Conclusion
In general, IMCs have made innovations in organization, management mechanism, exploitation of irrigation works creating favorable conditions for more effective performance of irrigation works, however, quality of enterprise governance of the companies is generally low. Production management organization lacks science, so production costs are still high, fuel consumption is high, and labor productivity is low. Companies do not have autonomy over labor, human resources, and salaries and most companies have not yet developed job placement schemes and salary payment mechanisms for workers. Recruitment, salary increase, promotion, arrangement and use of labor in the company depends on decision of the state.
Proposed solutions to improve governance quality of IMCs are solutions to perfect organizational structure and perfect enterprise governance mechanism. Companies must immediately innovate their management thinking, innovate management methods in the direction of fully exploiting potential advantages of irrigation infrastructure to increase revenue, thereby making better conditions to implement repair, maintenance and exploitation of irrigation works serving agriculture production and people’s livelihood.
REFERENCES
- Enterprise Law 59/2020/QH14, 2020
- Irrigation Law 08/2017/QH14, 2017
- General Department of Water Resources (2020). Report assessing situation of public irrigation management program
- PIM Center (2021). Report assessing current status of organizational model and operating mechanism of irrigation management organizations in relation to operation efficiency and financial autonomy
JOURNAL OF WATER RESOURCES SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY VIETNAM ACADEMY FOR WATER RESOURCESSPECIAL PUBLICATION NO 3 NOVEMBER 2023


